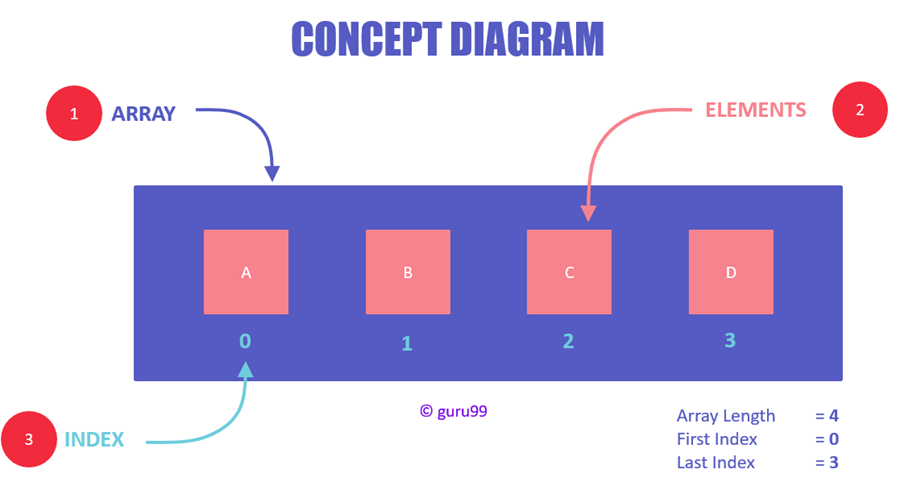
An array is a data structure for storing more than one data item that has a similar data type. The items of an array are allocated at adjacent memory locations. These memory locations are called elements of that array. The total number of elements in an array is called length.
The details of an array are accessed about its position. This reference is called index or subscript.

The above diagram illustrates that:
Note:
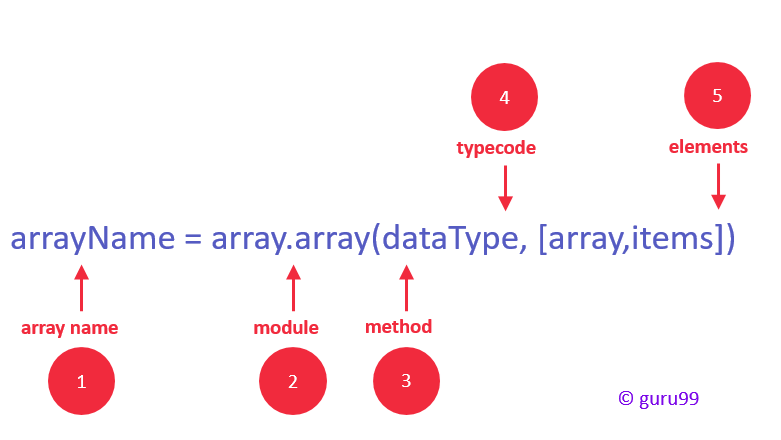
The following diagram illustrates the syntax of declaring an array in Python and C++ to present that the comprehension remains the same though the syntax may slightly vary in different languages.

Here, are some reasons for using arrays in data structure:
In Python, arrays are different from lists; lists can have array items of data types, whereas arrays can only have items of the same data type.
Python has a separate module for handling arrays called array, which you need to import before you start working on them.
Note: The array must contain real numbers like integers and floats, no strings allowed.
The following code illustrates how you can create an integer array in python to store account balance:
import array balance = array.array('i', [300,200,100]) print(balance)
You can declare an array in Python while initializing it using the following syntax.
arrayName = array.array(type code for data type, [array,items])
The following image explains the syntax.
The following table illustrates the typecodes available for supported data types:
| Type code | C Type | Python Type | Minimum size in bytes |
|---|---|---|---|
| ‘c’ | char | character | 1 |
| ‘B’ | unsigned char | int | 1 |
| ‘b’ | signed char | int | 1 |
| ‘u’ | Py_UNICODE | Unicode character | 2 |
| ‘h’ | signed short | int | 2 |
| ‘H’ | unsigned short | int | 2 |
| ‘i’ | signed int | int | 2 |
| ‘I’ | unsigned int | long | 2 |
| ‘l’ | signed long | int | 4 |
| ‘L’ | unsigned long | long | 4 |
| ‘f’ | float | float | 4 |
| ‘d’ | double | float | 8 |
You can access any array item by using its index.
Syntax
arrayName[indexNum]
Example:
balance[1]
The following image illustrates the basic concept of accessing arrays items by their index.

Here, we have accessed the second value of the array using its index, which is 1. The output of this will be 200, which is basically the second value of the balanced array.
import array balance = array.array('i', [300,200,100]) print(balance[1])
OUTPUT
The array module of Python has separate functions for performing array operations. This is a destructive method of operating with arrays, which means the modification will be saved in the array variable.
With this operation, you can insert one or more items into an array at the beginning, end, or any given index of the array. This method expects two arguments index and value.
Syntax
arrayName.insert(index, value)
Example:
Let’s add a new value right after the second item of the array. Currently, our balance array has three items 300, 200, and 100. So what’s the index of the second array item with a value of 200 if you said 1.
In order to insert the new value right “after” index 1, you need to reference index 2 in your insert method, like this:
import array balance = array.array('i', [300,200,100]) balance.insert(2, 150)
Now, to verify if the new value has been inserted, enter the array name and press Enter on the keyboard:
import array balance = array.array('i', [300,200,100]) balance.insert(2, 150) print(balance)
OUTPUT
array('i', [300,200,150,100])
With this operation, you can delete one item from an array by value. This method accepts only one argument, value. After running this method, the array items are re-arranged, and indices are re-assigned.
Syntax
arrayName.remove(value)
Example:
Let’s remove the value of 150 from the array. Currently, our balance array has four items 300, 200, 150, and 100. So, in order to remove 150 from the array, we only have to type 150 inside the method argument. Simple, right?
import array balance = array.array('i', [300,200,100]) balance.insert(2, 150) print(balance) balance.remove(150)
Now, to verify if the value has been deleted, enter the array name and press Enter on the keyboard:
import array balance = array.array('i', [300,200,100]) balance.insert(2, 150) print(balance) balance.remove(150) print(balance)
OUTPUT
array('i', [300,200,100])
With this operation, you can search for an item in an array based on its value. This method accepts only one argument, value. This is a non-destructive method, which means it does not affect the array values.
Syntax
arrayName.index(value)
Example:
Let’s search for the value of 150 in the array. Currently, our balance array has four items 300, 200, 150, and 100. So, in order to search 150 in the array, we only have to type 150 inside the method argument. That’s quite easy. This method returns the index of the searched value.
import array balance = array.array('i', [300,200,150,100]) print(balance.index(150))
OUTPUT
This operation is quite similar to the insert method, except that it will replace the existing value at the given index. This means will simply assign a new value at the given index. This method expects two arguments index and value.
Syntax
arrayName.udpate(index, value)
Example:
Assume that our array has four items 300, 200, 150, and 100, and we want to replace 150 with 145. So what’s the index 150?
Kudos, if you said 2.
In order to replace 150 that has index 2, you need to reference index 2 by using simple assignment operator, like this one:
import array balance = array.array('i', [300,200,150,100]) balance[2] = 145
Now, to verify if the value has been updated, enter the array name and press Enter on the keyboard:
import array balance = array.array('i', [300,200,150,100]) balance[2] = 145 print(balance)
OUTPUT
array('i', [300,200,145,100])
You can traverse a python array by using loops, like this one:
import array balance = array.array('i', [300,200,100]) for x in balance: print(x)
OUTPUT
300 200 100
C++ language is more flexible than Python when it comes to creating arrays. You can create C++ arrays in three ways mentioned ahead.
The following code illustrates how you can create an integer array in C++ to store account balance:
#include using namespace std; int main() < int balance[3] = < 300, 200, 100 >; for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) < cout return 0; >
You can declare an array in three syntax variants. Which one suits your program; this choice is based on your program requirements.
Declaration by Size
Syntax
dataType arrayName[arraySize];
Example:
int balance[3];
Declaration Initialization Array Items Only
Syntax
dataType arrayName[] = ;
Example:
int balance[] = < 300, 200, 100 >;
Declaration by Size and Initialization Array Items
Syntax
dataType arrayName[arraySize] = ;
Example:
int balance[3] = < 300, 200, 100 >;
You can access any array item by using its index.
Syntax
arrayName[indexNum]
Example:
balance[1]
The following image illustrates the basic concept of accessing arrays items by their index.

Here, we have accessed the second value of the array using its index, which is 1. The output of this will be 200, which is basically the second value of the balance array.
#include using namespace std; int main() < int balance[3] = < 300, 200, 100 >; coutUnlike Python, in C++ you have to program the logic yourself for performing the insert, delete, search update and traverse operations on C++ arrays.
The logic for insertion operation goes as follows:
In the following example, we have 5 items in the balance array, and we want to add a new item just after the value of 200. This means we have to shift all the items after 200 to a greater index, and then insert our new value of 150.
#include #include main() < int pos = 2; int size = 4; int balance[] = ; printf("BEFORE INCREMENT: \n"); for(int i = 0; i /* FOR SHIFTING ITEMS TO A GREATER INDEX */ for(int i = size; i >= pos; i--) < balance[i+1]=balance[i]; >/* FOR INSERTING VALUE AT OUR DESIRED INDEX */ balance[pos] = 150; printf("AFTER INCREMENT: \n"); /* FOR PRINTING THE NEW ARRAY */ for(int i = 0; i >
Output
BEFORE INCREMENT 300 200 100 50 0 AFTERINCREMENT 300 200 150 100 50 0
Lets create a programming in Java, in this array program in Java we will accept the size and the value of the array elements from the user.
import java.util.Scanner; public class AddElements < public static void main(String[] args) < Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Enter the size of the array"); int n=sc.nextInt(); int arr[]=new int[n]; System.out.println("Enter Elements in the array"); for(int i=0;iSystem.out.println("Elements in the array"); for(int j=0;j > >
Enter the size of the array 5 Enter Elements in the array 1 2 3 4 5 Elements in the array 1 2 3 4 5
Update an element by the given index.
Program in Java for how to Modify elements in an array
import java.util.Scanner; public class ModifyElement < public static void main(String[] args) < int arr[]=; int length= arr.length; Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Array Elements Before modify"); for(int i=0;i System.out.println("\nEnter the position where you want to change in an array"); int pos=sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("Enter the value"); int val=sc.nextInt(); arr[pos]=val; System.out.println("Array Elements After modify"); for(int j=0;j > >
Output:-
Array Elements Before modify 1 2 3 4 5 Enter the position where you want to change in an array 2 Enter the value 8 Array Elements After modify 1 2 8 4 5
Print all array elements.
Program in Java for how to Traverse in array
public class AccessElements < public static void main(String[] args) < int arr[]=; int length= arr.length; System.out.println("Array Elements are:-"); for(int i=0;i > >
Output:-
Array Elements are:- 1 2 3 4 5
You Might Like: